协会地址:上海市长宁区古北路620号图书馆楼309-313室
Towards AI4S 2.0: Shanghai AI Lab Open-Sources Intern-S1-Pro, the 1-Trillion-Parameter MoE Scientific Large Model
On February 4, Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory open-sourced Intern-S1-Pro, a 1-trillion-parameter multi-modal scientific large model built on SAGE—the technical architecture for the integration of general and specialized capabilities. This model serves as an innovative open systematic foundation for AI4S (AI for Science) to advance from the 1.0 era of the “tool revolution” to the 2.0 era of driving scientific discovery with “revolutionary tools”.
As the largest-parameter multi-modal scientific model in the global open-source community to date, Intern-S1-Pro has achieved a qualitative leap in its core scientific capabilities. It ranks internationally leading in AI4S for high-difficulty interdisciplinary evaluations, reaches the gold medal level of Olympiad competitions in complex mathematical and logical reasoning, and stands in the first echelon of open-source models in terms of agent capabilities for real-world research workflows.
The newly released Intern-S1-Pro represents a pivotal practice in building a specializable generalist model through SAGE. Based on the Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture, the model features 512 experts with a total of 1 trillion parameters, and only 8 experts (22 billion parameters) are activated per inference call. Its general and scientific capabilities evolve in synergy, with two core breakthroughs realized at the underlying architecture level:
- At the SAGE base model layer, the introduction of Fourier Position Embedding (FoPE) and the reconstruction of the temporal encoder endow the model with a “physical intuition” to uniformly understand signals ranging from micro-scale biological signals to macro-scale cosmic fluctuations.
- An efficient routing mechanism has systematically addressed the bottlenecks in training stability and computing efficiency for 1-trillion-parameter MoE models, laying a critical engineering foundation for the training of ultra-large-scale models.
Meanwhile, Intern-S1-Pro has validated a complete technical chain from original model architectures to an independently developed domestic computing power base, solidifying the underpinnings for building open and shared AGI4S (AGI for Science) infrastructure. Through open-sourcing, Intern-S1-Pro aims to lower the global research threshold and collaborate with academia and industry to drive a paradigm shift in scientific discovery powered by artificial general intelligence.
Online Demo: https://chat.intern-ai.org.cn
GitHub: https://github.com/InternLM/Intern-S1
HuggingFace: https://huggingface.co/internlm/Intern-S1-Pro
ModelScope: https://www.modelscope.cn/models/Shanghai_AI_Laboratory/Intern-S1-Pro
Innovative Underlying Architecture: Breaking the Boundaries of 1-Trillion-Parameter Scientific Models
Zhou Bowen, Director and Chief Scientist of Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, stated that the specializable generalist model is a feasible path to achieving artificial general intelligence (AGI). The key challenges for such models include:
- The need for low-cost, large-scale dense feedback during the training of specialized models;
- The ability to continuously learn and explore proactively, and to provide multi-perspective and multi-solution approaches to the same problem;
- The integration of physical world laws into model design, and the balancing of learning efficiency and performance across multiple differentiated capabilities.
Through a series of technical innovations at the SAGE base model layer, Intern-S1-Pro has expanded the boundaries of model applications, improved the feasibility of ultra-large-scale training, and advanced the exploration of specializable generalist models.
To build a scientific large model with a deeper understanding of the laws of the physical world, the research team introduced Fourier Position Embedding (FoPE) and reconstructed the temporal encoder. FoPE endows AI with a dual perspective: it can capture the relative distance between text tokens like observing “particles”, and grasp the overall laws and frequencies of scientific signals like analyzing “waves”. Scientific data and natural language also differ in terms of multi-scaling; the temporally encoder, which automatically adapts to data density, enables the model to uniformly process signals with sampling sizes ranging from a few to millions for the first time. This extends the model’s analytical scope from astronomy and geography to physiological signals, bioacoustics and other fields, achieving a major leap in perceptual capabilities.
To efficiently train the ultra-large 1-trillion-parameter model housing these capabilities, the research team innovated its internal routing mechanism. Traditional methods suffer from two critical pain points: inefficient training and computing resource waste. The new technology enables the model to learn more fully while operating efficiently through dense routing estimation, improving training stability. It then achieves load balancing across massive computing chips through a grouped routing strategy—similar to an intelligent traffic system—avoiding resource idleness. Through the synergistic innovation of algorithms and systems, the team has addressed the core bottlenecks in learning efficiency and resource scheduling for ultra-large-scale model training, laying a critical foundation for the efficient and robust training of the next generation of 1-trillion-parameter models.
With these underlying architectural innovations, Intern-S1-Pro has not only set a new upper limit for the parameter scale of multi-modal scientific models but also provided a implementable path for the “synergistic evolution of general and specialized capabilities” proposed by the SAGE architecture.
Scientific Capabilities Evolved Further, General Capabilities Advanced in Synergy
Benefiting from its innovative underlying architecture and 1-trillion-parameter ultra-large-scale training strategy, Intern-S1-Pro has achieved a further upgrade in scientific capabilities.
The model demonstrated competition-level problem-solving abilities in two authoritative benchmarks: the International Mathematical Olympiad Answer-Bench (IMO-Answer-Bench) and the 2025 International Physics Olympiad (IPhO2025).
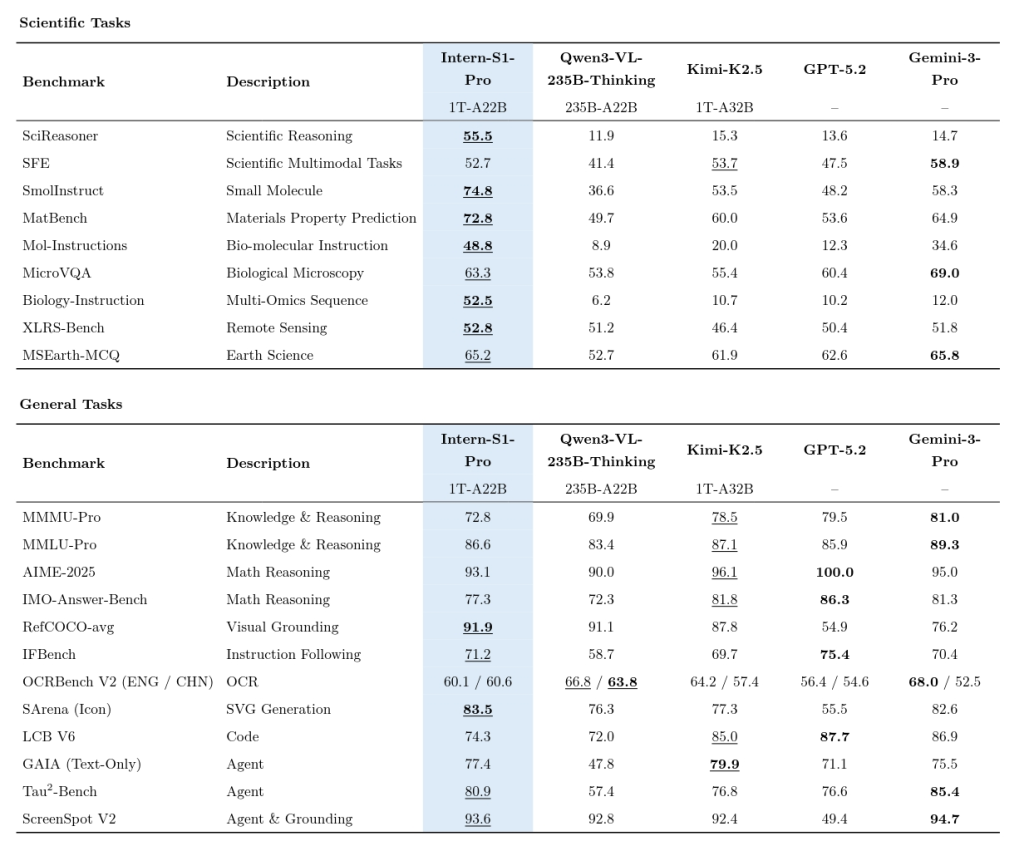
In key AI4S vertical fields, Intern-S1-Pro has successfully built a full-spectrum capability matrix spanning five core disciplines—chemistry, materials science, life science, earth science and physics—covering more than 100 professional subtasks. It has delivered excellent performance in single-discipline vertical evaluations such as Mol-Instructions and Biology-Instruction, and achieved comparable or even superior results to closed-source commercial large models and state-of-the-art (SOTA) vertical models in high-difficulty interdisciplinary evaluations such as SciReasoner, solidifying its position in the first echelon of the global AI4S field.
At the basic understanding level, Intern-S1-Pro can accurately parse complex molecular structure diagrams and various experimental charts with its high-precision multi-modal perceptual capabilities. At the logical reasoning level, it can handle advanced scientific Q&A (e.g., reaction condition inference, physical and chemical property prediction) and accurately capture the causal laws behind data. With the continuous enhancement of its understanding and reasoning capabilities, the model’s capability boundary has expanded to real-world research scenarios, with its applications ranging from micro-scale tasks such as chemical retrosynthesis and protein sequence generation to macro-scale complex tasks such as remote sensing image analysis. Evaluations in real research scenarios such as XLRS-Bench have demonstrated the model’s research productivity value—evolving from “solving problems” to “addressing research challenges”—and provided solid support for cutting-edge scientific exploration.
Meanwhile, through the technical route of integrating general and specialized capabilities, Intern-S1-Pro has realized the synergistic advancement of general and professional scientific capabilities. It ranks in the first echelon of open-source models in core dimensions including cross-modal image-text understanding, scientific chart logical reasoning, multi-scenario visual perception, high-quality natural language generation and precise complex instruction following, demonstrating solid and comprehensive overall strength.
The training strategy of integrating general and specialized capabilities has enabled Intern-S1-Pro to not only address the shortcomings of traditional cutting-edge models in professional reasoning but also achieve the balanced development of multi-modal and text general capabilities. This truly materializes the synergistic evolution of general and professional scientific capabilities, providing reliable support for the understanding, reasoning and application of complex problems in research scenarios.
In terms of agent capabilities, Intern-S1-Pro has achieved a leap from “static task planning” to “dynamic environmental interaction”. It has reached an internationally leading level in the Tau²-Bench, which centers on dynamic environments and complex interactions, laying a solid foundation for empowering complex scientific agents.
Building a Unified “Computing Power-Algorithm” Foundation
While scaling up and improving performance, Intern-S1-Pro has built an original unified “computing power-algorithm” foundation. From the initial stage of architecture design, the model established a joint R&D route with the Ascend computing ecosystem, achieving in-depth full-stack adaptation from the underlying operators and compilation optimization to the upper-layer training and inference frameworks.
The R&D team has addressed a series of core technical challenges in large-scale training, including precision alignment, stability of long-sequence reinforcement learning and the ultimate release of hardware performance. Through the refined optimization of the XTuner V1 training framework and the efficient deployment of the LMDeploy inference engine, combined with advanced memory management and parallel strategies, the team has ensured the efficiency and stability of 1-trillion-parameter model training. The application of innovative technologies such as the fully asynchronous reinforcement learning framework has greatly improved training efficiency and reduced R&D costs and thresholds. In addition, Intern-S1-Pro has jointly developed model acceleration operator adaptation with Muxi Technology, laying a solid foundation for open and shared future AGI4S infrastructure.
High-Quality Open-Sourcing Empowers an Innovative Ecosystem
Since the first release of the InternLM series in 2023, Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory has gradually built a rich family of InternLM large models, including the multi-modal scientific model Intern-S1, the large language model InternLM, the multi-modal model InternVL and the high-reasoning model InternThinker. The laboratory has also pioneered and open-sourced a full-chain open-source tool system for large model R&D and application, covering key links such as data processing, pre-training, fine-tuning, deployment, evaluation and application. Core tools including the training framework XTuner, deployment and inference framework LMDeploy, evaluation framework OpenCompass, high-efficiency document parsing tool MinerU and the deliberative AI search application MindSearch have all been fully open-sourced, forming a vibrant open-source community with the participation of hundreds of thousands of developers.
Since its release, Intern-S1 has repeatedly topped the global multi-modal model rankings on HuggingFace, with cumulative downloads exceeding 410,000 and nearly 200 research institutions and enterprises applying for cooperation. Its outstanding cross-modal scientific understanding capabilities have not only provided an efficient tool for scientific research but also lowered the threshold for global research teams to embrace AGI for Science through open-sourcing. Going forward, based on research paradigm innovation and model capability improvement, Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory will continue to open-source Intern-S1 and its full-chain tool system, support free commercial use, and provide online open services to co-build a more open and efficient scientific AI ecosystem with global partners.
References
① Fourier Position Embedding: Enhancing Attention’s Periodic Extension for Length Generalization (https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.17739)


